Hand washing hand hygiene info Chemical Man
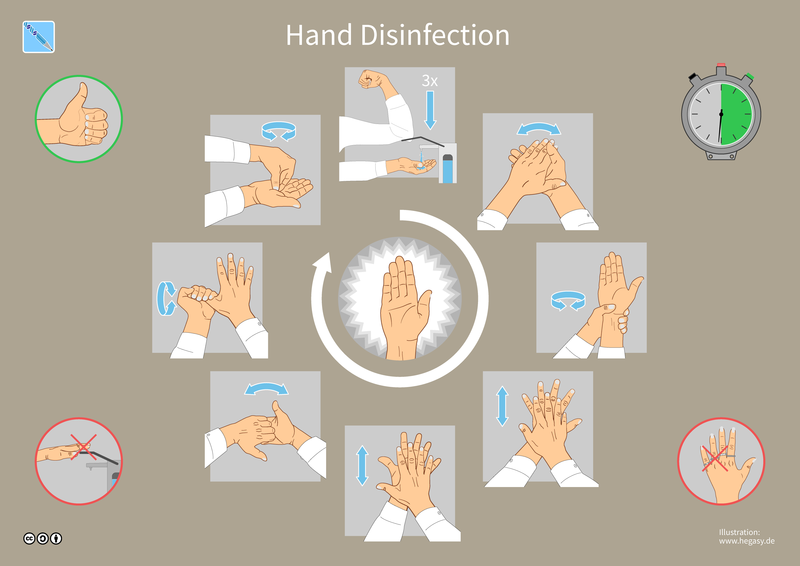
Hand washing, also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning hands for the purpose of removing soil, dirt, and microorganisms. If water and soap is not available, hands can be cleaned with ash instead. A substitute for tap water is pouring water from a hanging jerrycan or gourd.
Medical hand hygiene refers to hygiene practices related to medical procedures. Hand washing before administering medicine or medical care can prevent or minimize the spread of disease. The main medical purpose of washing hands is to cleanse the hands of pathogens (like bacteria or viruses) and chemicals which can cause harm or disease. This is especially important for people who handle food or work in the medical field, but also important practice for the general public.
Handwashing with soap consistently at critical moments during the day prevents the spread of diseases like diarrhoea and cholera which are transmitted through fecal-oral routes. People can become infected with respiratory diseases such as influenza or the common cold, for example, if they do not wash their hands before touching their eyes, nose, or mouth.
Health benefits
Hand washing has the following health benefits:
helps minimize the spread of influenza
diarrhea prevention
avoiding respiratory infections
a preventive measure for infant deaths at their home birth deliveries
improved hand washing practices have been shown to lead to small improvements in the length growth in children under five years of age
In developing countries, childhood mortality rates related to respiratory and diarrheal diseases can be reduced by introducing simple behavioral changes, such as hand washing with soap. This simple action can reduce the rate of mortality from these diseases by almost 50 percent.
Interventions that promote hand washing can reduce diarrhoea episodes by about a third, and this is comparable to providing clean water in low income areas.Furthermore, 48% reductions in diarrhoea episodes can be associated with hand washing with soap.
Hand washing with soap is the single most effective and inexpensive way to prevent diarrhea and acute respiratory infections (ARI), as automatic behavior performed in homes, schools, and communities worldwide. Pneumonia, a major ARI, is the number one cause of mortality among children under five years old, taking the life of an estimated 1.8 million children per year. Diarrhea and pneumonia together account for almost 3.5 million child deaths annually. According to UNICEF, turning hand washing with soap before eating and after using the toilet into an ingrained habit can save more lives than any single vaccine or medical intervention, cutting deaths from diarrhea by almost half and deaths from acute respiratory infections by one-quarter. Hand washing is usually integrated together with other sanitation interventions as part of water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) programmes.
Handwashing also protects against impetigo which is transmitted through direct physical contact.
A possible small detrimental effect of hand washing is that frequent hand washing can lead to skin damage due to drying of the skin. Excessive hand washing is commonly seen as a symptom of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).

Leave a comment